 |
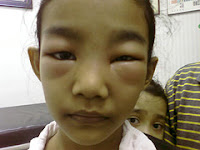
| Puffiness of eyes in nephrotic syndrome |
Nephrotic Syndrome is a kidney disorder which is characterized by:
1. Abnormal protein leak
2. Low levels of proteins in blood (due to protein leakage)
3. Increased levels of lipid
4. Swelling of body parts (called edema).
Symptoms of Nephrotic Syndrome:
- Edema (swelling) of the face, limbs, or abdomen
- Foamy urine
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight gain
- oliguria
As nephrotic syndrome progresses, other symptoms may develop including:
- Cough
- Difficult or painful urination
- Fever
- Headache
- Hematuria (blood in urine)
- Respiratory Distress
Causes Of Nephrotic Syndrome:
Primary Glomerulonephritis
- Membranous Glomerulonephritis
- Minimal change disease
- Focal segmental Glomerulonephritis
- Membranoprolifirative Glomerulonephritis
- IgA nephropathy
Systemic diseases with renal manifestations
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Amyloidosis
- SLE
- Infections ( Malaria, syphilis, hepatitis B, HIV )
- Allergy
- Ill effects of drugs (e.g. antibiotics like penicillin or drugs given to control blood pressure)
- Malignancy
- Psychological factors
- Idiopathic (Unknown causes)
Risk Factors:
- Certain cancer medications
- Family history of autoimmune disorders
- Personal history of autoimmune disorders
- Recent infection
Investigations:
- Urine analysis
- Blood analysis
- Kidney biopsy
Diagnosis:
An individual, who shows the symptoms of Nephrotic disorder, is subjected to a blood test and urine test to measure the amount of protein, cholesterol and sugar in the blood. More sophisticated tests like ultrasound, CT scan, and MRI can be performed for accurate detection of the disorder. A biopsy of the kidney can also be helpful in determining the extent of damage suffered by the organ.
Any ways, diagnosis should be made on the basis of following:
1. History
2. Physical Examination
3. Investigations
Diet For The Patients Of Nephrotic Syndrome:
Diet is as follows:


Treatment Plan:
Treatment of nephrotic syndrome depends on the cause of the disease and may include:
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone or prednisolone, to reduce swelling.
Diuretics, such as bumetanide (Bumex) or furosemide (Lasix), to reduce fluid buildup in the body (edema) and help with reducing sodium, potassium, and water. Fluid reduction should occur slowly to avoid further kidney damage and low blood pressure.
In rare cases, salt-free albumin given through a vein (IV). Albumin helps remove extra fluid from the tissues.
Treatment for nephrotic syndrome depends on the cause and the age of the person who has the condition. Medicines, changes in diet, and care for other conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, are all possible treatments for this syndrome. These treatments may reverse, slow or prevent further kidney damage.








.jpg)





 Posted in:
Posted in:
4 comments:
There are new method for nephritic syndrome, without dialysis and kidney transplant.
Hello! Someone in my Facebook group shared this website with us so
I came to look it over. I'm definitely enjoying the information. I'm bookmarking and will be tweeting this to my followers! Exceptional blog and terrific design.
Also visit my blog Adrenal Fatigue Neurasthenia
gud info..:)
What's up it's me, I am also visiting this web page regularly, this web site is genuinely good and the users are in fact sharing
pleasant thoughts.
Feel free to surf to my blog post Green coffee
Post a Comment